What Is a Mortgage Discharge Fee?

For many homeowners, finalizing their mortgages marks a key point in their housing journey. It comes as a surprise to most borrowers that completing mortgage payments does not void the claim of the lender over the property. Homeowners must go through a mortgage discharge procedure to be relieved of mortgage obligation. This guide details the Canadian mortgage discharge fee structure and the best practices that minimize these expenses, sparing homeowners financial stress with mortgage discharge.
What Is a Mortgage Discharge Fee?
Homeowners need to pay a mortgage discharge fee to their lender after their mortgage ends for the total mortgage balance payment and cancellation of property title ownership rights. After the mortgage payment in full, the lender charges a cost that completes the necessary legal and administrative tasks to finalize the mortgage.
According to Victoria Ishai , Mortgage agent at Clover Mortgage: “All financial institutions maintain similar standard charges according to location as well as mortgage type and lender-defined policies.”
Mortgage payments do not automatically end for homeowners because lenders need to commence formal legal steps for releasing their property interests. The necessary official documents and administrative duties for mortgage termination require payment of discharge fees by homeowners.
Homeowners need to distinguish mortgage discharge fees from prepayment penalties because mortgage discharge fees are standalone costs from the penalties that apply when borrowers pay their mortgage early. Switching between payment of mortgage prepayment penalties and formal discharge fees requires homeowners to understand the differences so they can prevent unwanted expenses when their mortgage term ends.
Why Do Mortgage Discharge Fees Exist?
The payment of mortgage discharge fees enables lenders to operate and manage the administrative process of mortgage terminations. This includes:
- Legal documentation processing enables the lender's property claim removal.
- The financial institution makes sure all procedures match provincial requirements governing land title records.
- The administrative account closure process performed internally by staff members completes the requirements to close accounts.
- Financial institutions determine discharge fees differently from each other which customers usually find written in their initial mortgage agreement. Understanding these advance costs beforehand enables borrowers to construct proper financial plans.
Key Factors Affecting Mortgage Discharge Fees in Canada
Here are some of the key factors that determine how much Canadians must pay for their mortgage discharge fees:
- Lender Policies: Mortgage rate policies set by financial institutions establish their discharge fees between $50 and more than $400 depending on the institution. Mortgage lenders may add extra administrative costs specifically when borrowers terminate their mortgage contracts before the original agreement. Borrowers need to check their mortgage contracts because lenders establish different fees for mortgage discharge services.
- Provincial Regulations: surrounding real estate transactions by province causes mortgage discharge fees to differ between provinces. Standards for mortgage fees exist at a provincial level since certain provinces authorize lenders to establish their rates. Both Ontario and British Columbia impose higher discharge fees than Alberta and Manitoba since these provinces face elevated regulations that generate administrative costs during legal processing.
- Mortgage Type and Termination Timing: The fee paid to close a mortgage depends on whether it is being terminated at a specific time or not. Early mortgage payoff causes borrowers to pay extra charges which consist of prepayment penalties and the mandatory discharge fee. The standard administrative costs represent the only financial burden lenders charge borrowers who finish their mortgage according to plan.
- Additional Legal Fees: A mortgage discharge process through professional legal assistance beyond standard lender operations can lead to secondary payment expenses. Borrowers often need to get a real estate lawyer involved to complete the title transfer process from the lender specifically when working with private lenders or complicated mortgage agreements.
Mortgage Discharge Fees Across Canada
Each province together with each lending institution sets its specific mortgage discharge fee rates. Discharge fees follow these standard averages in numerous provinces of Canada.
| Province | Average Discharge Fee |
|---|---|
| Ontario | $200 - $400 |
| British Columbia | $75 - $400 |
| Alberta | $50 - $300 |
| Quebec | $200 - $300 |
| Manitoba | $75 - $250 |
| Nova Scotia | $100 - $350 |
Strategies to Reduce Mortgage Discharge Fees
The mortgage discharge fees are traditional payments in this industry but some alternatives exist to potentially cancel or lower them:
- Refinancing Incentives: the lenders pay the discharge fee costs if you choose to refinance through them instead of transferring to another lender institution.
- Loyalty Programs: Commitment programs within loyalty initiatives provide long-term clients with fee-cutting opportunities or total fee eliminations.
- Timing Considerations: The timing of your mortgage payoff should match your mortgage term to prevent the onset of early termination penalties that would lead to additional fees.
- Compare Lenders: It is important to research different financial institutions since some lenders present mortgage options featuring lower discharge fees which enhances your selection process of mortgage providers.
Mortgage discharge fee negotiations should be considered with lenders before finalizing the mortgage cancellation process despite not every lender performing these negotiations.
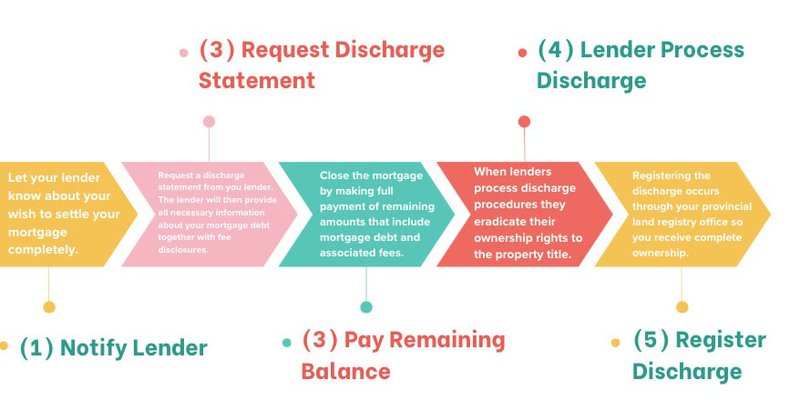
Steps to Discharging a Mortgage
Below is an accurate timeline of the mortgage discharge process:
Conclusion
The mortgage discharge fee stands as a vital expense that homebuyers need to handle their mortgage termination in Canada. An awareness of fee structures and possible fee negotiation and non-payment effects will enable homeowners to handle mortgage termination processes more effectively. People who take out mortgages must develop a strategy to conduct cost comparisons between lenders and obtain legal advice if needed to reduce unneeded costs.
Contact Clover Mortgage today to learn how to best navigate the mortgage discharge process and minimize associated fees.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a mortgage discharge fee, and why do I need to pay it?
A mortgage discharge fee is an administrative fee that lenders charge their borrowers to officially remove their title claim from the property after complete mortgage repayment. The payment of this fee ensures official documentation will release your property owner rights from lenders.
How much can a mortgage discharge fee cost in Canada?
Customers need to pay between $50 and $400 as mortgage discharge fees except when specific lenders decide to waive these costs. Every mortgage agreement should include all extra charges from lenders which include legal or processing fees. Inspect your mortgage agreement to get full details on every fee.
Are mortgage discharge fees negotiable?
In some cases, yes. Locking in certain lenders' special deals including customer loyalty and refinancing agreements will sometimes lead to waiving the required fee.
What happens if I don’t pay the mortgage discharge fee when paying off my mortgage?
Defaulting on the discharge fee results in document transfer delays, possible legal troubles, and extra penalties.





